Recently, the Journal of Medicinal Chemistry (IF: 8.039), a top journal in the field of medicinal chemistry,published the latest research of Prof. Cheng Jiang's team and Prof. Qinghua Hu's team: Discovery of a Series of 5-Amide-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxyl Derivatives as Potent P2Y14R Antagonists with Anti-Inflammatory Characters. Master Degree candidate Yuhang Wang and Doctoral candidate Mengze Zhou are the co-first authors of this paper. Professor Cheng Jiang , Professor Qinghua Hu and Associate Researcher Lili Xu are the co-corresponding authors of this paper, and China Pharmaceutical University is the sole correspondent of this paper.
The purinergic receptor (P2Y) is widely distributed in the body, mainly activated by endogenous purines or pyrimidines and their glycosides, and is thought to play an important role in the development of many diseases. In a previous study, the group revealed the regulatory role of P2Y14R in intrinsic immune cell death and confirmed the feasibility of P2Y14R as a potential target for acute inflammation-related diseases. However, the reported P2Y14 receptor antagonists have a single structure, among which the highly selective and active PPTN is represented, but PPTN is difficult to be further developed due to its extremely low solubility and bioavailability.
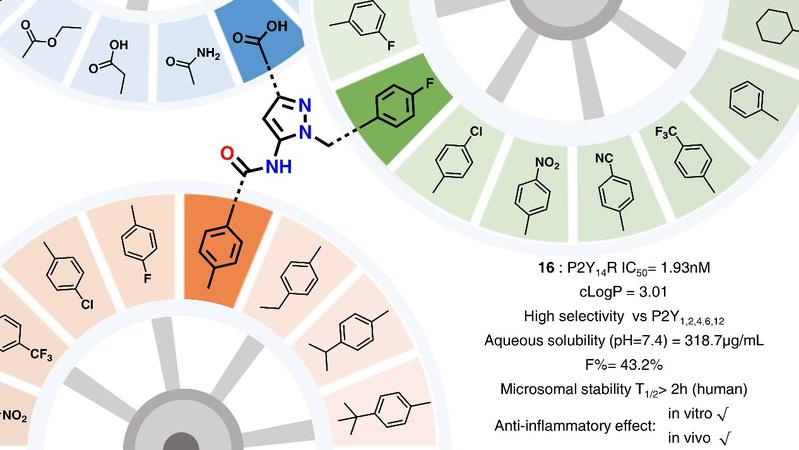
In this study, based on the previous work of the group, a series of 5-amino-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxylic acid derivatives were designed and synthesized by using a backbone leap design strategy. After decomposition of the groups with important roles with the receptor in the structure of P2Y14 receptor antagonist, the dominant fragment structures suitable for each binding region were explored, and the dominant fragment structures were integrated to obtain compound 16. The high inhibitory activity and high selectivity of compound 16 on P2Y14 receptor were confirmed by screening HEK293 cells expressing different receptors. To verify the binding ability of the designed compound to P2Y14 receptor, the group designed and synthesized a P2Y14 receptor fluorescent antagonist as a probe, and demonstrated the strongest binding ability of compound 16 by flow cytometry method. The study showed that the obtained compound 16 exhibited significantly improved physicochemical properties such as solubility, good pharmacokinetic characteristics such as in vitro and in vivo metabolic stability and bioavailability, and had superior drug-forming properties. As verified by cellular and animal experiments, compound 16 exhibited excellent in vitro and in vivo anti-inflammatory activity and can be used as a candidate compound for further development.
This study is a cross-collaboration between the disciplines of medicinal chemistry and pharmacology, and is jointly advanced. The results of the research work may provide guidance for the research of novel P2Y14 receptor antagonists and potential therapeutic agents for inflammatory diseases such as peritonitis and sepsis.
The work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant (82073685, 81773745, 81872867 and 82173675), the Jiangsu Provincial Key Laboratory of Marine Drug Compound Screening (HY2011902), the Jiangsu Provincial Youth and Blue Project Fund (2632021ZD13) and the Fundamental Research Funds of Central Universities.
Article link: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.2c01632