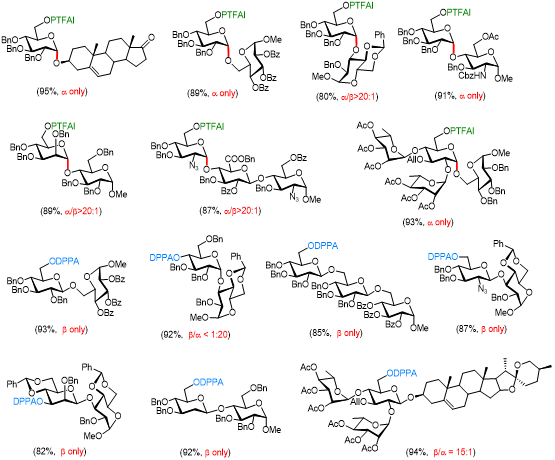
The configuration of the anomeric glycosidic linkages is crucial for maintaining the biological functions and activities of carbohydrate molecules. However, their stereochemistry control in glycosylation represents one of the most challenging tasks in carbohydrate chemistry. Recently, Li’s group reported that N-phenyltrifluoroacetimidoyl (PTFAI), a well-known leaving group for catalytic glycosylation, can act as a stereodirecting group for the challenging 1,2-cis α-glycosylation. Utilizing rapidly accessible 1,6-di-OPTFAI glycosyl donors, TMSOTf-catalyzed glycosylation occurred with excellent α-selectivity and broad substrate scope, and the remaining 6-OPTFAI group can be cleaved chemoselectively. The remote participation of 6-OPTFAI is supported by the first characterization of the crucial 1,6-bridged bicyclic oxazepinium ion intermediates by low-temperature NMR spectroscopy. These cations were found to be relatively stable and mainly responsible for the present stereoselectivities. Further application is highlighted in glycosylation reactions toward trisaccharide heparins as well as the convergent synthesis of chacotriose derivatives using a bulky 2,4-di-O-glycosylated donor.
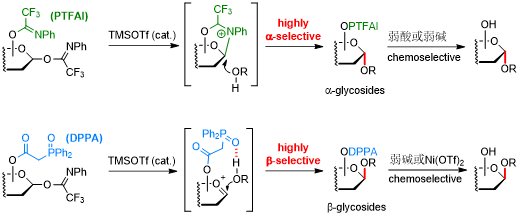
One the other hand, Li’s group has also developed another remote-directing group, namely DPPA, to synthesize the complementary β-glycosides via hydrogen-bond mediated delivery of the alcoholic acceptors. TMSOTf-catalyzed glycosylation with DPPA-installed glycosyl imidate donors displayed excellent β-selectivities and broad substrate scope, particularly practical to synthesize the challenging β-configured 2-deoxy and 2-azido-2-deoxy glycosides from poor acceptors suffering from electron-deficiency, steric hindrance, and structural rigidity. Chemoselective removal of the DPPA group could be readily achieved under the mild catalysis of Ni(OTf)2 without affecting acid- or base-labile functional groups, facilitating a rapid conversion to biologically important molecules such as uronic acids and 2,6-deoxy glycosides. The application of this DPPA-directed glycosylation was further highlighted in the complex synthesis toward saponin dioscin using 2,4-O-glycosylated donor in a convergent manner.
These results have been published on Angewandte Chemie International Edition and Chinese Journal of Chemistry, respectively.
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/anie.202201510
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/cjoc.202100865


