Recently, ACS Nano (impact factor 18.027), the top journal in the field of nanotechnology, published the latest achievements on the detection of tumor cell membrane surface markers, which researched by Professor Zheng Feng and Professor Wang Huai-Song from the Department of Pharmaceutical Analysis, School of Pharmacy at China Pharmaceutical University. The title is: Lanthanide Complexes for Tumor Diagnosis and Therapy by Targeting Sialic Acid. Master Degree candidate Wang Jiali and Master Degree candidate Hu Xinyuan are the co-first authors of this article. Professor Zheng Feng and Professor Wang Huaisong are the corresponding authors of this article.
The identification and detection of tumor cell membrane surface markers is of great significance for the diagnosis and treatment of tumor diseases. Sialic acid (SA) is a kind of negatively charged acidic polysaccharide composed of nine-carbon skeleton, which exists at the chain terminals of glycoproteins or glycolipids on the cell membrane and participates in cell recognition, adhesion, information transmission, division, differentiation and other life activities. A large number of studies have shown that when a variety of inflammatory diseases or malignant carcinogenesis occur in the body, the expression of SA on the cell membrane of the inflammatory site or tumor site is significantly higher than the normal level, and the up-regulation of SA metabolism also increases the blood SA level. Therefore, accurate and sensitive determination of sialic acid content is of great significance for auxiliary diagnosis of tumor.
This work synthesized a series of lanthanide-containing bimetallic complexes (TDA-M-Lns) with fluorescent lanthanide ion (Ln3+=Tb3+, Eu3+, Dy3+, Sm3+), metal ion quencher (M2+=Cu2+, Co2+) and organic ligand (2,2 '-thiodiacetic acid (TDA)) for SA sensing. SA can competitively coordinate with Ln3+, resulting in the signal-on of Ln3+, so as to realize the detection of SA in blood samples by TDA-M-Lns. Among TDA-M-Lns, TDA-Co-Eu showed the highest sensitivity for SA detection in blood of tumor-bearing mice. In addition, TDA-Co-Eu can deposit Eu3+ on the surface of tumor cells by targeting SA on the surface of tumor cell membrane, and inhibit the growth and migration of tumor cells, which provides a new idea for the treatment of tumor diseases.
The work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China and the Basic Research Funds of Central universities.
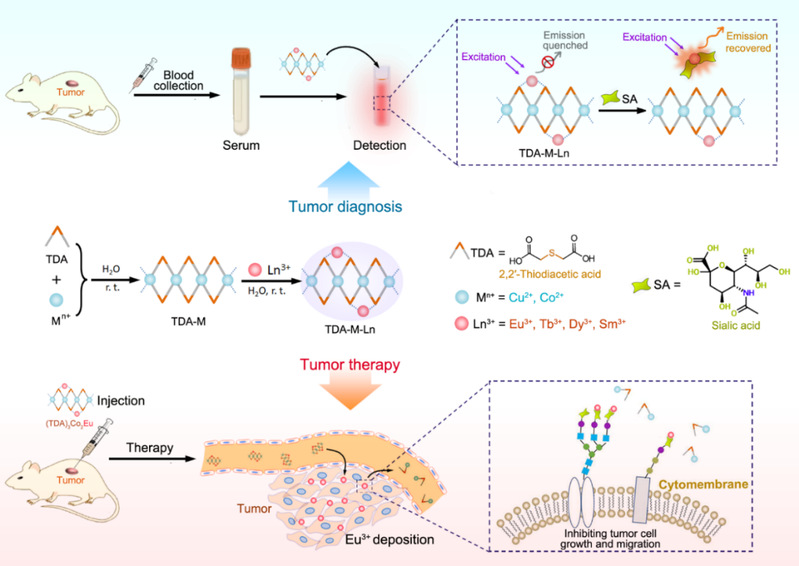
Schematic illustration of TDA-M-Lns for fluorescent detection of S A and tumor treatment.
Article link: https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.2c05715


