Graduate students:
|
|
Pengbo Zhao (2021-) | Ying Zhu (2021-) |
|
|
Jingyu Dai (2023-) | Huanyu Qin (2023-) |
Gene delivery, LNP synthesis, polypeptide synthesis, nanomedicine, nanovaccine, tissue regeneration, autoimmune disease
1. Research Projects
(1)High-level talent program of China Pharmaceutical University, 2021-2027,1000,000 RMB
(2)Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province: “Intestinal lymphatic transport-adipose niche metabolism regulation oral lipid nanovaccine in acute myeloid leukemia”, 2022-2025,200,000 RMB
(3)National Center of Technology Innovation for Biopharmaceuticals, “Multi-barrier breaking based oral nanovaccine in gene delivery”, 2022-2025,500,000 RMB
(4)National Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program for Undergraduate, “Application of biodegradable elastin-like polypeptides in gene delivery and wound healing”. 2022-2023
2. Academic Awards
Weierman excellent thesis of China Pharmaceutical University, 2019, Rank first
3. Representative Research Achievements
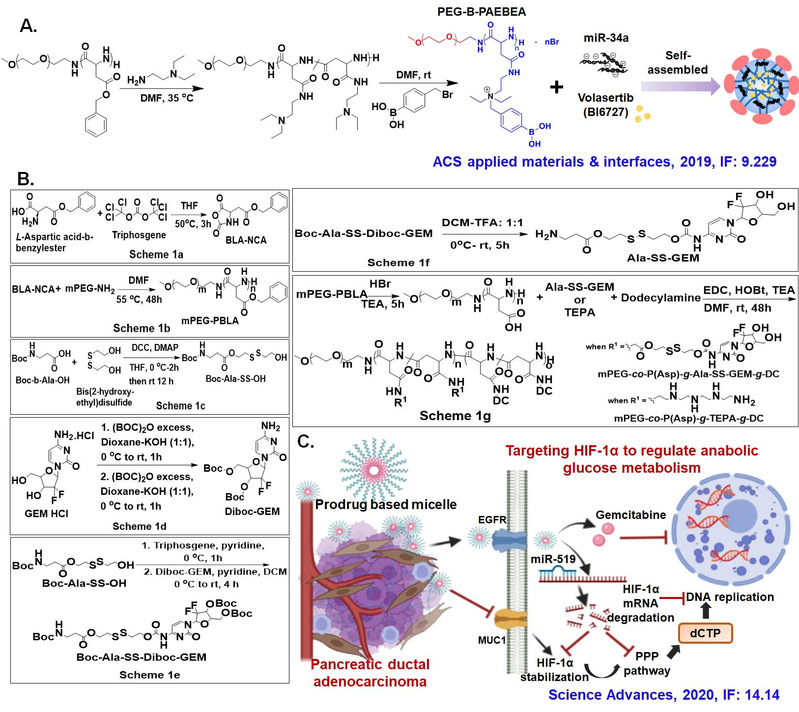
(1) Desmoplastic and hypoxic pancreatic cancer microenvironment induces aberrant expression of miRNAs and hypoxia-inducible factor-1 (HIF-1α) responsible for gemcitabine (GEM) resistance. We demonstrated that miR-519c was down-regulated in pancreatic cancer and transfection of miR-519c in GEM-resistant pancreatic cancer cells inhibited HIF-1α level under hypoxia. We synthesized redox-sensitive mPEG-co-P(Asp)-g-DC-g-S-S-GEM polymer, with GEM payload of 14% (w/w) and 90% GEM release upon incubation with l-glutathione. We synthesized mPEGco-P(Asp)-g-TEPA-g-DC for complex formation with miRNA. Chemical modification of miR-519c with 2′-O-methylphosphorothioate (OMe-PS) at 3′ end enhanced its stability and activity without being immunogenic. Epidermal growth factor receptor targeting peptide GE11 decoration increased tumor accumulation of micelles after systemic administration and significantly inhibited orthotopic desmoplastic pancreatic cancer growth in NSG mice by down-regulating HIF-1α and genes responsible for glucose uptake and cancer cell metabolism. Our multifunctional nanomedicine of GEM and OMe-PS–miR-519c offers a novel therapeutic strategy to treat desmoplasia and hypoxia-induced chemoresistance in pancreatic cancer.
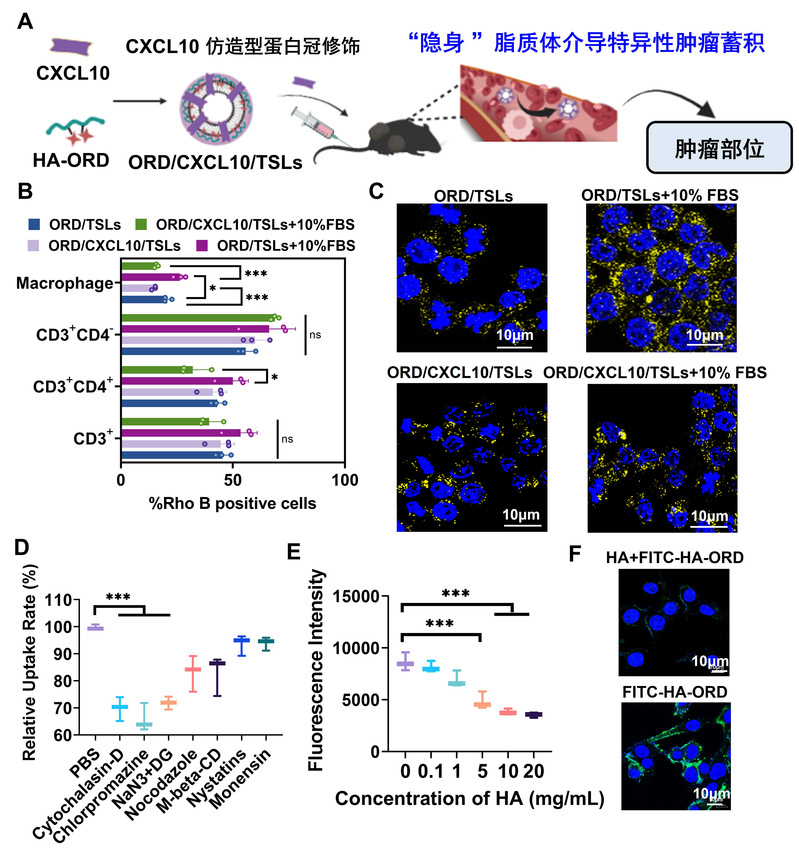
(2) The interplay of liposome-protein corona hinders the clinical application of liposomes due to active macrophage sequestration and rapid plasma clearance. Here we showed that, CXCL10 as a therapeutic protein was coronated the thermosensitive liposomes to form stealth-like nanocarriers (CXCL10/TSLs). Decoration of the corona layer of CXCL10/TSLs by hyaluronic acid conjugated oridonin (ORD/CXCL10/TSLs), overcame the “fluid barrier” built by biological proteins, drastically reduced capture by leukocytes in whole blood, allowed the specific targeting of tumor sites. Multifunctional medicine ORD/CXCL10/TSLs with hyperthermia drove the sustained cytokine-CXCL10 inflammatory loop to switch macrophage phenotype to M1-like, expand tumor-infiltrating natural killer cells and induce intratumoral levels of interferon-γ. Oridonin synergized with CXCL10 during ORD/CXCL10/TSLs treatment, downregulated PI3K/AKT and Raf/MEK signaling for M1-like polarization and migration inhibition. Furthermore, ORD/CXCL10/TSLs potently synergized with anti-PD-L1 antibody in mice bearing metastatic melanoma, induced sustained immunological memory and controlled metastatic spread.
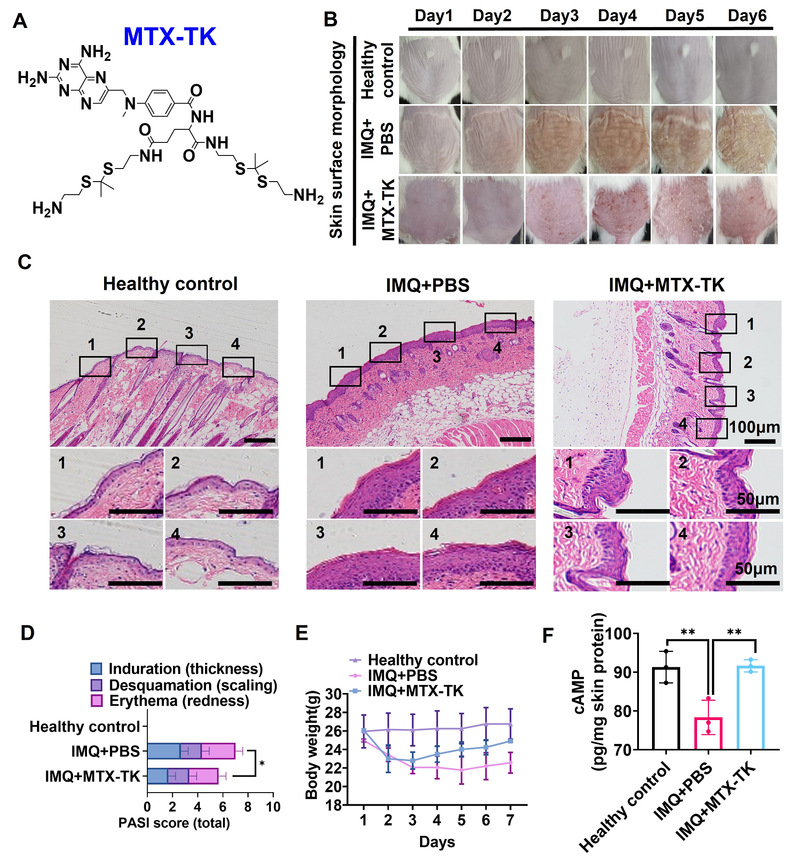
(3) Oxidative stress, nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB) and adenosine signaling are factors associated with the psoriatic inflammation. Topical delivery of methotrexate (MTX) has become an option to overcome the side effects caused by systemic therapy in psoriasis, leading to the suppression of NF-κB activation through boosting adenosine release. However, the thickened psoriatic skin is the primary restriction against the local drug delivery. The nanoassemblies-loaded microneedle arrays were capable of significantly penetrating the imiquimod-induced psoriatic epidermis in mice. The efficient topical delivery of these nanoassemblies was achieved by potent mechanical strength and hyaluronic acid as the dissolvable matrix for microneedle arrays. CD44-mediated endocytosis enabled the intracellular uptake of nanoassemblies in keratinocytes, and methotrexate was released from MTX-TK-HA with ROS stimuli, followed by suppressing the proliferation of epidermal cells via NF-κB pathway blockade. In psoriatic mouse model, nanoassemblies loaded microneedle arrays relieved the inflammatory skin disorders via regulation of adenosine and NF-κB signaling. Our study offered a rational design for the transdermal delivery of hydrophobic agents and defined an effective therapeutic option for psoriasis treatment.
1. Xiaofei Xina,#, Jingjing Lia,#, Wantao Wua,#, Lianjie Rena,d, Pengbo Zhaoa, Ying Zhua, Chao Qina,*, Lifang Yina,b,c,* “ROS-scavenging Nanomedicine for “Multiple Crosstalk” Modulation in Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease”. Biomaterials science. 2023, accepted. (IF 7.590)
2. Zhou, Yong, Lei Yang, Yifu Lyu, Di Wu, Ying Zhu, Jingjing Li, Dabo Jiang, Xiaofei Xin*, and Lifang Yin*. Topical Delivery of ROS-Responsive Methotrexate Prodrug Nanoassemblies by a Dissolvable Microneedle Patch for Psoriasis Therapy. International Journal of Nanomedicine (2023): 899-915. (IF 7.033)
3. Xiaofei Xin, Yong Zhou, Jingjing Li, Kai Zhang, Chao Qin, and Lifang Yin. CXCL10-coronated thermosensitive “stealth” liposomes for sequential chemoimmunotherapy in melanoma. Nanomedicine: Nanotechnology, Biology and Medicine 48 (2023): 102634. (IF: 6.458)
4. Jiang, Dabo, Yang Yang, Xiuyi Yang, Boxuan Wang, Wenxuan Fan, Yuchen Liu, Xiaofei Xin*, and Lifang Yin*. The application of elastin-like peptides in cancer, tissue engineering and ocular disease. OpenNano 9 (2023): 100113.
5. Xin, Xiaofei, Qiyue Wang, Virender Kumar, Ajit S. Narang, and Ram I. Mahato. Protein and Peptide Delivery to the Lung via Inhalation. In Organ Specific Drug Delivery and Targeting to the Lungs, pp. 453-484. CRC Press, 2022. (Book Chapter)
6. Kumar, Virender, Xiaofei Xin, Jingyi Ma, Chalet Tan, Natalia Osna, and Ram I. Mahato. Therapeutic targets, novel drugs, and delivery systems for diabetes associated NAFLD and liver fibrosis. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews (2021): 113888. (IF: 15.47)
7. Xiaofei Xin, Virender Kumar, Feng Lin, Vinod Kumar, Rajan Bhattarai, Vijaya R. Bhatt, Chalet Tan, and Ram I. Mahato. Redox-responsive nanoplatform for codelivery of miR-519c and gemcitabine for pancreatic cancer therapy. Science advances 6, no. 46 (2020): eabd6764. (IF: 14.14)
8. Xiaofei Xin, Feng Lin, Qiyue Wang, Lifang Yin, and Ram I. Mahato. ROS-Responsive Polymeric Micelles for Triggered Simultaneous Delivery of PLK1 Inhibitor/miR-34a and Effective Synergistic Therapy in Pancreatic Cancer. ACS applied materials & interfaces 11, no. 16 (2019): 14647-14659. (IF: 9.229)
9. Xiaofei Xin, Chao Teng, Xiaoqing Du, Yaiqi Lv, Qingqing Xiao, Yubing Wu, Wei He, and Lifang Yin. Drug-delivering-drug platform-mediated potent protein therapeutics via a non-endolysosomal route. Theranostics 8, no. 13 (2018): 3474. (IF: 11.60)
10. Xiaofei Xin, Xue Pei, Xin Yang, Yaqi Lv, Li Zhang, Wei He, and Lifang Yin. Rod-shaped active drug particles enable efficient and safe gene delivery. Advanced Science 4, no. 11 (2017): 1700324. (IF: 17.52)
Graduate students:
|
|
Pengbo Zhao (2021-) | Ying Zhu (2021-) |
|
|
Jingyu Dai (2023-) | Huanyu Qin (2023-) |







