Recently, the team of Prof. Dai Jianjun/Ju Yanmin from our school published their latest research results in Nano Letters (IF=10.8), a top journal with the title: Bimetallic Nanozyme, a Credible Tag for In Situ-Catalyzed Reporter Deposition in the Lateral Flow Immunoassay for Ultrasensitive Cancer Diagnosis。 Postgraduate student Meng Xiangming, and PhD student, Zuo Wanchao of our school, are the co-first authors of this paper. Prof. Dai Jianjuni, Associate Researcher Ju Yanmin of our school, together with the assistant Researcher Zhang Donghui, Zhanjiang Central People's Hospital, Guangdong Province are the co-corresponding authors. CPU is the unique correspondence affiliation.
Cancer markers often have diverse degrees of variability in the early stages of cancer development. Their presence or alteration can be indicative of the tumour progression. Therefore, rapid and sensitive monitoring of these biomarkers is essential for early screening, treatment and prognostic monitoring of cancer. Lateral flow immunochromatography (LFIA) is one of the most popular methods for immediate diagnosis, and has been applied in the fields of food safety testing, environmental monitoring, as well as especially early diagnosis of diseases. Since the outbreak of COVID-19, LFIA has also played an increasingly important role in disease diagnosis and pandemic prevention and control. However, conventional colorimetric LFIA (e.g., colloidal gold LFIA) has limited sensitivity and quantitative ability to be read by the naked eye, imposing on them with a very limited application in low concentration biomarker detection.
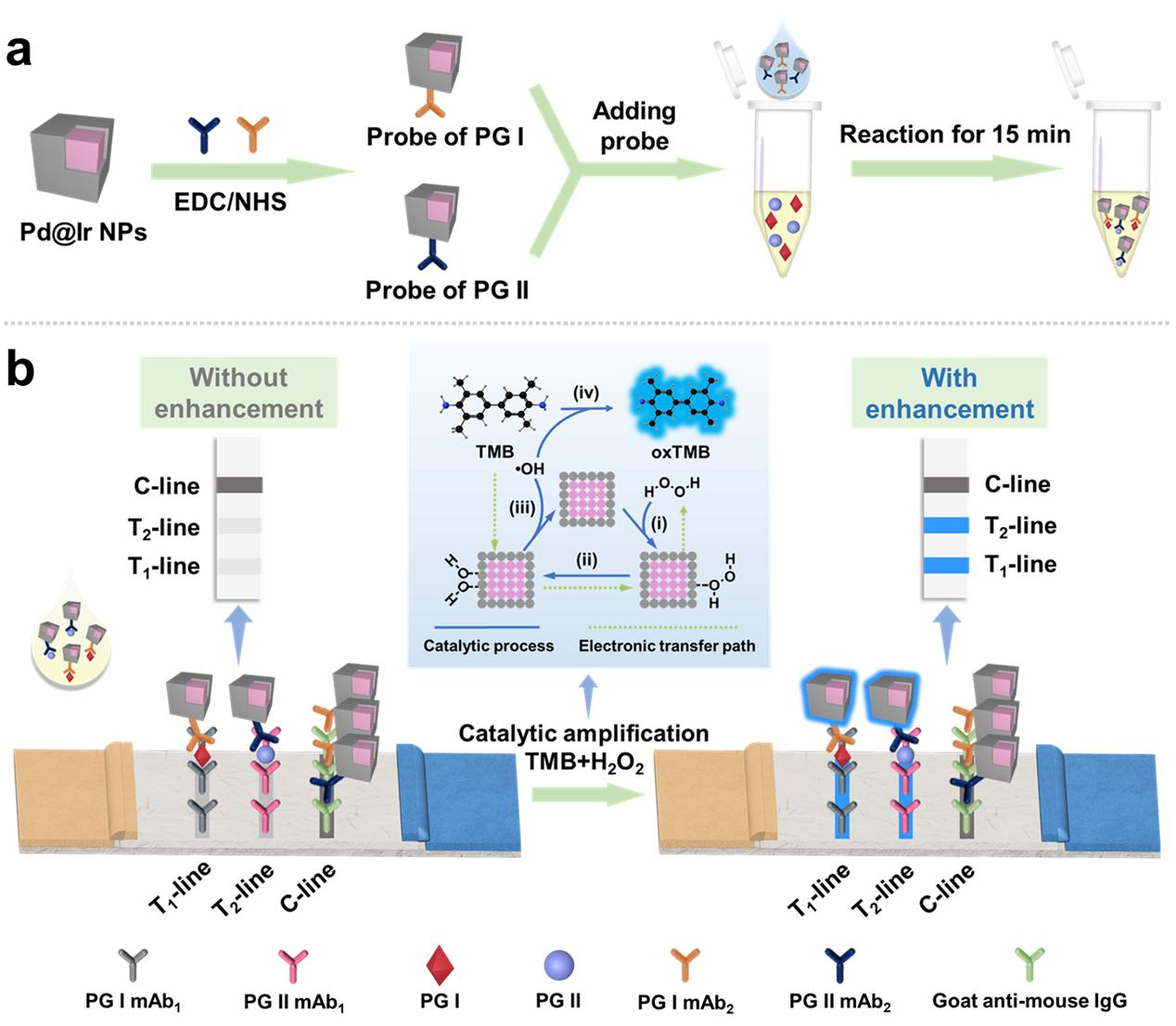
To address these issues, the research team employs a colourimetric signal amplification strategy, i.e., bimetallic nanozyme-mediated in situ-catalyzed reporter deposition (BN-ISCRD), for LFIA to achieve ultrasensitive detection of cancer biomarkers. Due to the synergistic or additive effect of the two metals, the bimetallic nanoenzymes (Pd@Ir NPs) exhibit superior peroxidase-like activities than Pd NPs and Ir NPs. Based on this, they are taken as labelling materials for LFIA by in situ catalytic reporter molecule deposition in order to achieve the amplification of colorimetric signals and enhance the detection sensitivity. The method is applied to the detection of gastric cancer markers (PG I and PG II), and the naked-eye detection limit is up to 10 pg/mL after signal amplification, providing a 200-fold sensitivity. In parallel, 8 gastric cancer-positive samples have been successfully identified from 36 clinical serum samples, in line with the detection results of the clinical method. This BN-ISCRD strategy combines novel nanomaterials with biosensing technology to introduce a new approach for building an ultrasensitive and instantaneous detection platform.
The work was sponsored by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2021YFA0910200), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 52002402, No. 32172855), and the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (No. BK20200574).
Original link: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.nanolett.3c03118